Climate History
Climate changes in the deep past of Earth provides strong evidence that we
are in a committed global warming planetary emergency.
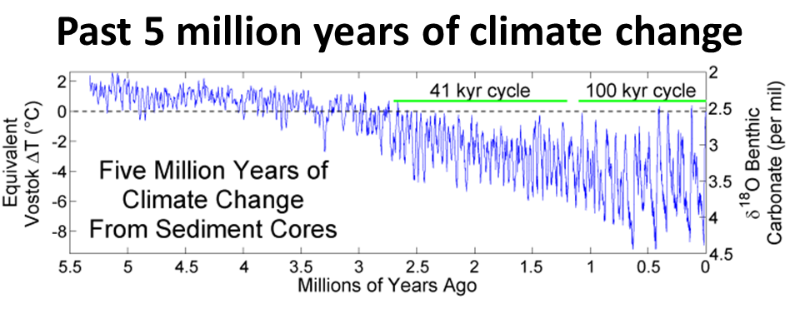
The WMO (2017) and latest research April 2019 (Mid-Pleistocene transition in glacial cycles, 2019 W. Williet confirms that atmospheric CO2 is the highest in at least 3-5 million years.
are in a committed global warming planetary emergency.
The WMO (2017) and latest research April 2019 (Mid-Pleistocene transition in glacial cycles, 2019 W. Williet confirms that atmospheric CO2 is the highest in at least 3-5 million years.
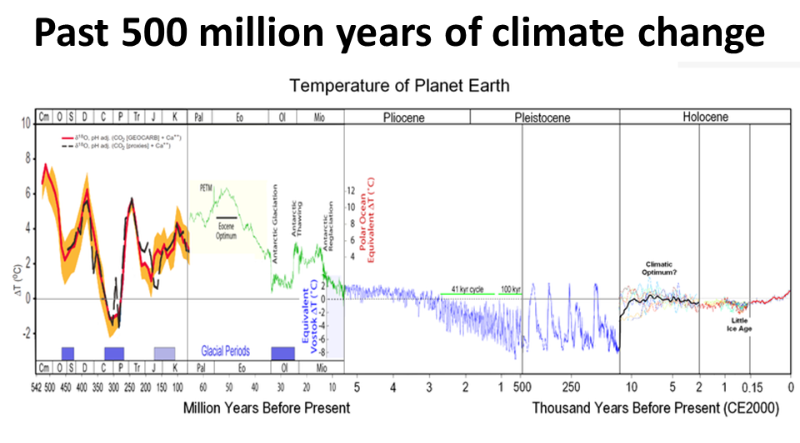
The same research confirms that over this time period surface temperatures have never reached 2C higher than the pre-industrial degree.
Scientists can tell the state of past climates by examining ice cores, animal and plant fossils, preserved pollen and tree rings.
2009 research had found that atmospheric CO2 could be the highest in 15 million years.
Scientists can tell the state of past climates by examining ice cores, animal and plant fossils, preserved pollen and tree rings.
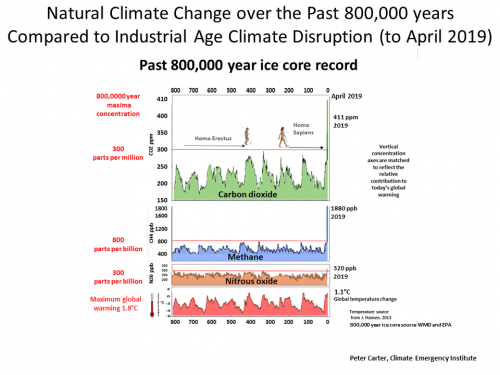
The deepest ice core from Antarctica goes back 800,000 years
Global temperatures and atmospheric CO2 concentrations have been much higher in the deep past.
However the ice cores show that today's atmospheric CO2 methane is far higher than any time in the past 800,0000 years. The rate of global warming today is extremely high.
Atmospheric CO2 (411 ppm April 2019) is 37% higher than its 800,000 year limit (300 ppm).
Atmospheric methane (1800 ppb) is 160% or over two and a half times higher that its pre-industrial level(722 ppb).
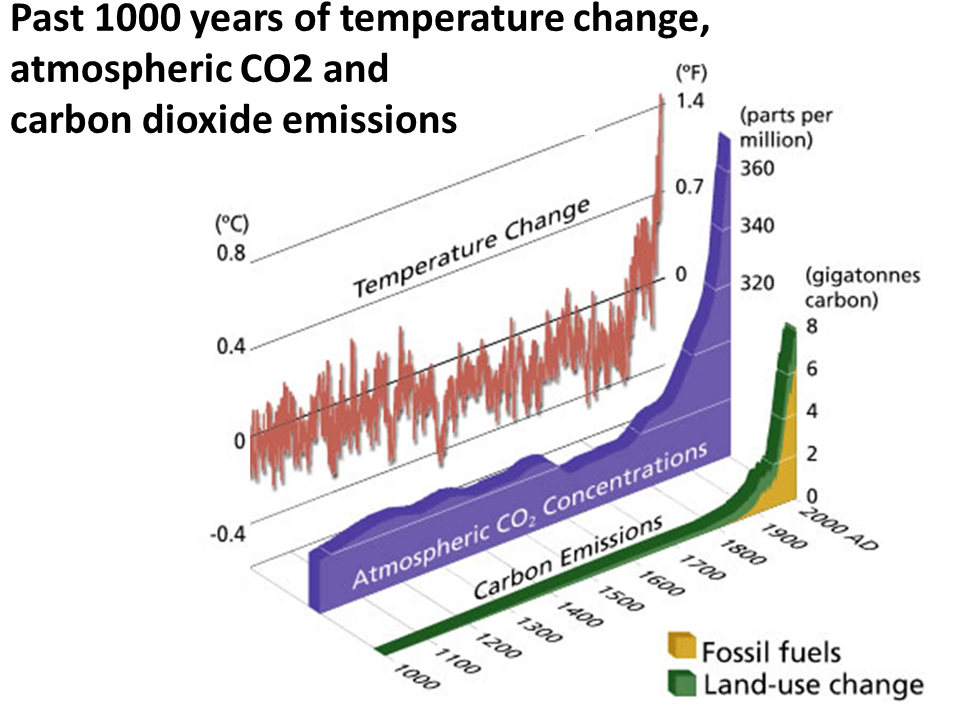
Furthermore the rate of increase in atmospheric CO2 is unprecedented (IPCC and WMO).
Multiple lines of evidence show that the rate at which CO2 has increased in the atmosphere during 1900–2019 is at least 10 times faster than at any other time during the last 800,000 years (high confidence), and 4–5 times faster than during the last 56 million years. IPCC AR6 WG1{5.1.1, 2.2.3; Figures 5.3, 5.4; Cross-Chapter Box 2.1}
Multiple lines of evidence show that the rate at which CO2 has increased in the atmosphere during 1900–2019 is at least 10 times faster than at any other time during the last 800,000 years (high confidence), and 4–5 times faster than during the last 56 million years. IPCC AR6 WG1{5.1.1, 2.2.3; Figures 5.3, 5.4; Cross-Chapter Box 2.1}

Allianz (Insurance) Climate timeline - A short history of the Earth's climate
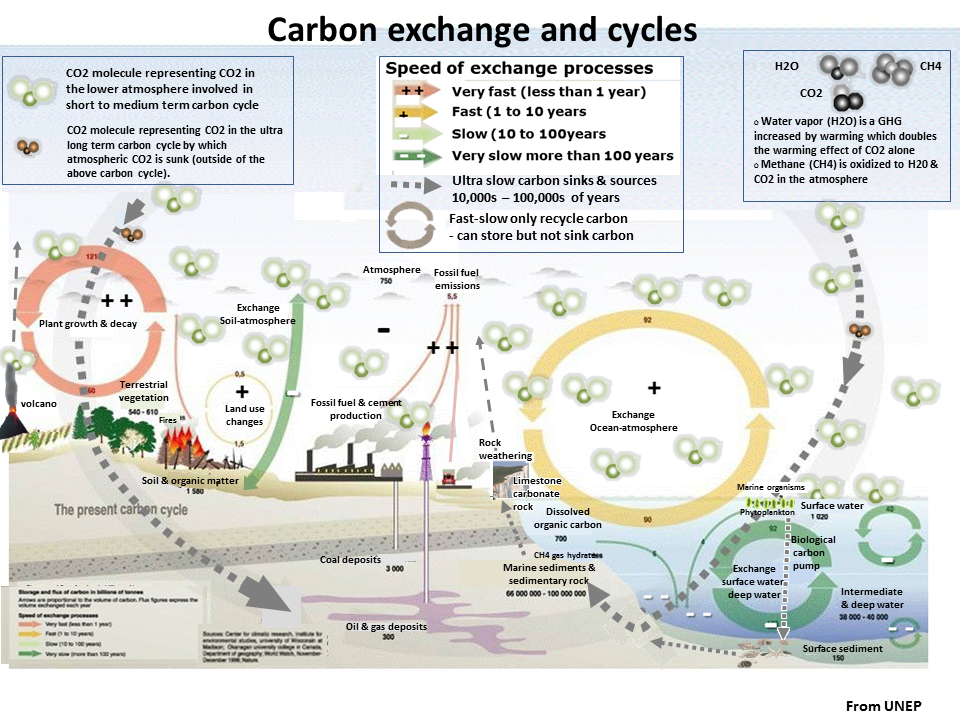
Over millions of years the climate is controlled by the sinking of carbon from atmospheric CO2.
What we call fossil fuels are the land fossil carbon sinks that has allowed live oxygen dependent life to evolve to the great biodiversity of today. Most of the Earth coal deposits are 250 million years old or more.
The land carbon sink of fossil carbon has been reversed by industrialized civilization burning coal oil and gas.
What we call fossil fuels are the land fossil carbon sinks that has allowed live oxygen dependent life to evolve to the great biodiversity of today. Most of the Earth coal deposits are 250 million years old or more.
The land carbon sink of fossil carbon has been reversed by industrialized civilization burning coal oil and gas.
The only carbon sink now is the ocean that sinks carbon as carbonate rock- limestone and dolomite, over 100,000s of years.
The only carbon sink now is the ocean that sinks carbon as carbonate rock- limestone and dolomite, over 100,000s of years.